Treatment of appendicitis: drugs and surgery
The mainstay of treatment in acute appendicitis is almost always surgery. Its role is to prevent rupture of the appendix.
Postponement of surgery is a consideration in mild and chronic forms or in people with high operative risk or postoperative complications (simultaneous occurrence of several diseases in a person's old age).
With conservative management, bed rest, antibiotic (venous) therapy and infusion therapy, diet and regular monitoring of the development of the discomfort at short intervals (ultrasound, CT, inflammatory parameters) are important.
The conservative form is characterised by a lower success rate and frequent relapses (recurrence) within the first year.
The surgical solution can be performed as a classical open surgery - appendectomy at laparotomy or as a less invasive (minimally invasive) technique - laparoscopically.
Laparotomy is the classic open method: it is guided by an incision in the area of McBurney's point. It is chosen mainly when complications occur, but also when the cause of the difficulty is unclear.
The procedure is performed through a created hole in the abdominal wall, through which the worm-like protrusion is removed. Subsequently, after healing, a surgical scar of about 6 centimetres is left on the abdominal wall.
Laparoscopy is a more gentle form. It has several advantages, such as reduced risk of infection, less pain, smaller surgical wounds, faster post-operative recovery and therefore shorter sick leave (PN). However, it requires technical equipment and skill of the operator.
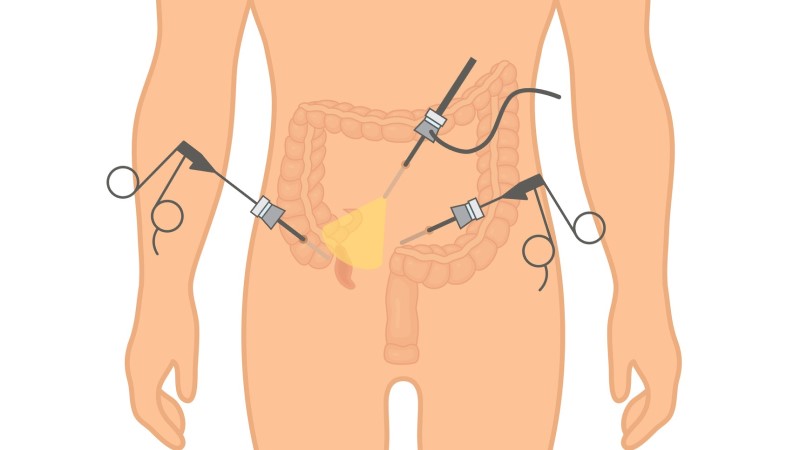
There was no significant difference between the two techniques.
Postoperative treatment includes prophylactic antibiotic treatment, bed rest, diet and plenty of fluids. Postoperatively, the person is fasted for 24 hours. It starts with fluids and a liquid diet and gradually solid food is added.
The course can be complicated by the confinement of inflammation, i.e. the formation of an abscess. This must initially be aspirated or a puncture performed under ultrasound or CT control. ATB treatment is supplemented. Subsequently, with an interval of months, surgery is chosen.










