Alopecia: Treatment is both outpatient and at home. Topical and general medication
In the first place, we must concentrate on discovering the cause of the disease. In the next step, the doctor will choose the treatment according to the type of alopecia and according to gender. In the following section, we will describe the options for topical and general treatment of alopecia. Also, the proper care of our hair.
Topical treatment
In the topical treatment of alopecia, a dermal solution is often used that contains 2 drugs: prednisolone (a synthetic corticosteroid/corticoid) and salicylic acid.
Prednisolone is used to reduce the inflammation of the hair follicle. Salicylic acid can act in concentrations up to 0,5 %, in particular by facilitating the penetration of other drugs. It is also keratolytic and has an anti-inflammatory effect.
Salicylic acid also has a weak antimicrobial effect on Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, pathogenic yeasts, moulds and dermatophytes.
Dosage and dosage schedule:
The dermal solution is applied 1 time a day (preferably in the evening). When the inflammatory symptoms have subsided, it is sufficient to apply the solution 2 to 3 times a week. It is applied with the applicator with the opening facing downwards and gently moved over the affected areas.
The duration of treatment depends on the type and course of the disease and is determined individually by the doctor. Due to the corticosteroid content, the solution should not be applied to small areas for more than 2 to 3 weeks.
Minoxidil
It is usually available on the market in the form of a solution. It is especially intended for men who suffer from hair loss or weakening of the hair on the top of the head, and women with general weakening of the hair.
Minoxidil has a complex effect on the hair follicle and prolongs the growth phase. Its effect is only temporary. After the treatment is stopped, hair loss occurs again.
Minoxidil should not be used alone, but in combination with other topical drugs. For example, with 0.05% all-trans retinoic acid, topical corticosteroid, anthralin or total corticosteroids.
Method of application of minoxidil solution:
The solution should be applied only to dry hair and scalp. Apply one dose of the dermal solution directly to the scalp at the site of hair loss twice daily (morning and evening). Spread the dose over the entire affected area and massage it into the skin with your fingertips.
Total treatment
Antiandrogens
Antiandrogens are used only in the treatment of alopecia in women. In men, antiandrogens are contraindicated due to their mechanism of action. In the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in women, drugs that have the following effects are used:
- reduce the action of androgens (male sex hormones)
- increase the level of SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin), which carries androgens in the blood
- stimulate the hair growth phase
- reduce the length of the resting phase of the growth cycle
In practice, the drug cyproterone acetate is used. It suppresses the effect of androgens, which are formed in small quantities in the female organism. It also has a gestagenic and antigonadotropic effect.
In a woman, it reduces:
- pathologically increased body hair (hirsutism)
- hair loss conditioned by androgens (androgenic alopecia)
- increased activity of the sebaceous glands (in acne and seborrhoea)
Spironolactone
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic. It is structurally similar to aldosterone, which has an antiandrogenic effect. Its antiandrogenic effect is provided by reducing testosterone levels and blocking androgen receptors in the target tissue. Spironolactone slows hair loss but does not stimulate hair growth.
What is the dosage?
The dose of spironolactone ranges from 50 mg daily with gradual dose increases of 50 mg at monthly intervals until a cumulative dose of 200 mg daily is reached. Treatment should last at least 6 months.
Side effects of spironolactone:
- Menstrual cycle disorders
- postmenopausal bleeding
- hyperkalaemia
- weakness
5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
The enzyme 5-alpha-reductase is found in two forms in the human body. The first form is found in the sebaceous glands, liver, skin and capillitium. The second form is found in the prostate and some areas of the terminal hair.
5-alpha-reductase inhibitors regulate the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone in the cells of the dermal papilla of the follicular unit. 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors include the drugs finasteride and dutasteride.
Finasteride is used in practice for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. During testing, its beneficial effects on hair have been found. Finasteride is most effective on hair in the frontal region and on the top of the head. However, the effect of treatment is not permanent, it is washed out of the body approximately one month after the end of treatment. After 6 months, the condition of the hair returns to its original level.
Finasteride is not recommended for use in women.
Dutasteride is a dual 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor that is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia. The recommended daily dose is 0.5 mg for several years.
The effect of treatment appears in about 12 months. According to research papers, it is more effective than finasteride.
Both finasteride and dutasteride are prescription drugs prescribed by a urologist. They have serious side effects:
- loss of libido
- erectile dysfunction
- psychological problems
Other treatment options
Other treatment options for alopecia include mesotherapy, hair transplantation, laser therapy and stem cell transplantation.
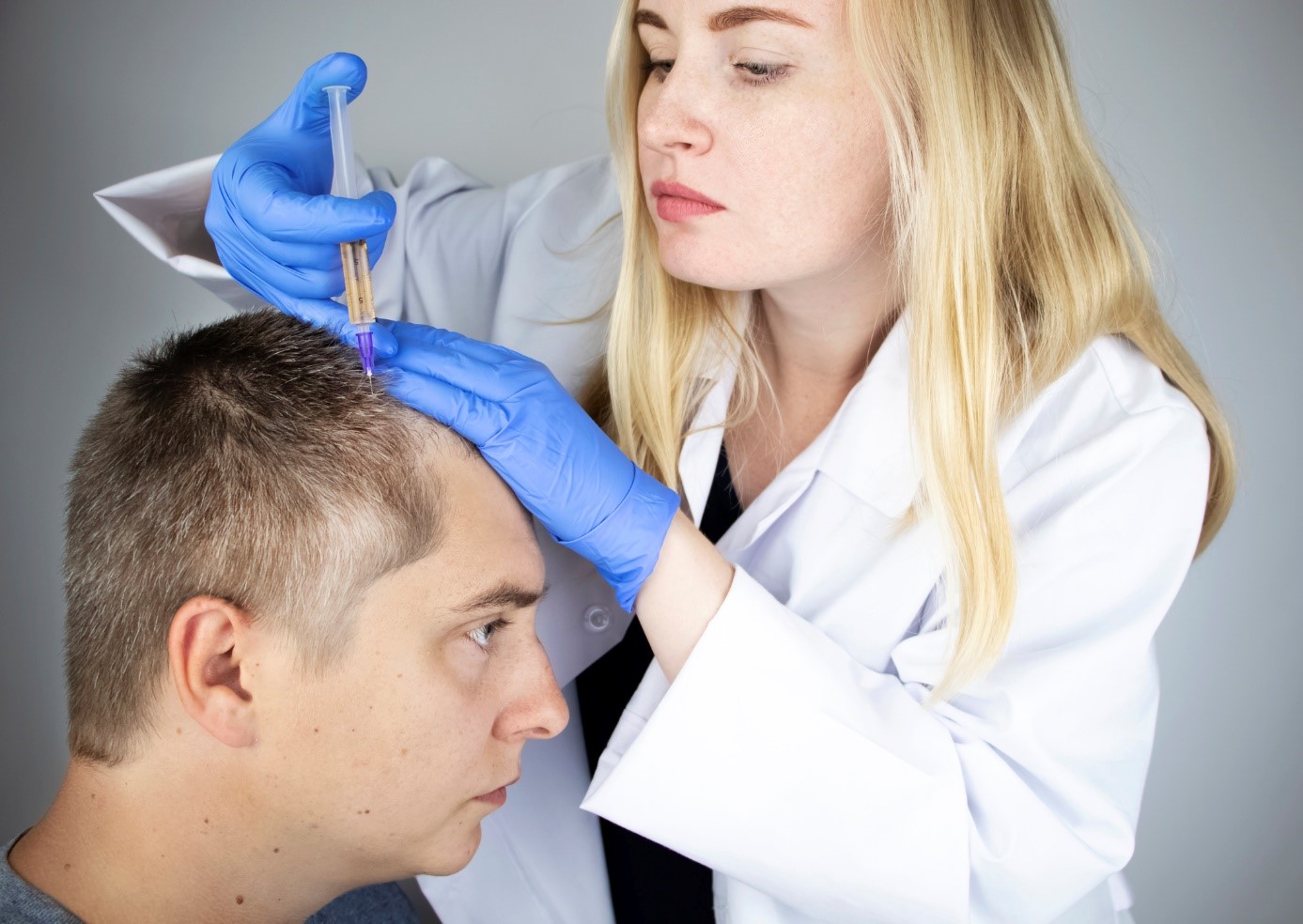
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy is a minimally invasive method that is used in the treatment of alopecia in both men and women. In this method, a revitalizing solution is injected into the skin using a mini-injection technique. The solution contains the following ingredients:
- 4 biomimetic patented peptides - revitalizes existing hair, promotes the formation of new hair
- complex of 13 vitamins - beneficial effects on skin and hair follicle revitalization
- 24 amino acids - helps to create a hair follicle
- 5 minerals - protect the skin from adverse influences, help absorb nutrition
- 4 coenzymes - revitalize hair roots
- 4 nucleic acids - block the effects of stress and other adverse influences
- 2 reducing agents - help collagen formation in the hair, purify the scalp
Hair growth promotion, increased blood circulation and prolongation of the growth phase are provided not only by the applied solution, but also by the reflex stimulation caused by the injections themselves.
Side effects of mesotherapy:
- Inflammation
- infection
- allergic reactions
Hair transplantation
For many patients, this method is economically unaffordable. The result of the transplant should be nice looking hair. This type of treatment is referred to as invasive surgery.
Hair transplantation is based on the removal of grafts from areas that are not sensitive to the influence of androgens. Hair transplanted in this way is not subject to local hormonal influences, which ensures its permanent growth and survival.
The disadvantage of this treatment method is that it cannot stop the loss of the surrounding hair. It may happen that the grafts are preserved in the frontal area while the surrounding hair falls out.
Laser treatment
The exact mechanism of action of lasers in the treatment of alopecia is not known. It is believed that they stimulate the hair roots and their transition from the resting phase to the growth phase, prolonging the growth phase and promoting cell division in the hair roots during the growth phase.
Stem cell transplantation
This form of treatment is only suitable for the early stages of alopecia.
Stem cell transplantation is one of the semi-invasive treatment methods. In the treatment of alopecia, stem cells that are isolated from fat or hair follicles are mainly used. The cells obtained in this way are processed in a special device and then injected deep into the problem alopecia zone in the form of a liquid suspension.










