Stinging in the ear: from a draft or from the cervical spine? There are several causes...

Pain in the ear is a symptom of disease in the ear itself, but this is not always the case. Sometimes it originates elsewhere and only radiates to the ear. However, the highest percentage of these pains originate in the ear. The earache is just a symptom.
Pain in the ear (otalgia) is another symptom that can indicate several diseases. One case is pain caused by a local disease in the ear. This can be inflammation of the ear canal, the middle ear, but also the inner ear or inflammation of the skin in the area.
The second type is characterized by pain transmitted to the ear, i.e., pricking in the ear from another area. This type of pain is also characterized as radiating pain. It is also the cause of several diseases. As an example, it also arises in tooth pain, cervical spine.
A pinching in the ear is most often a symptom of a disease of the ear canal or middle ear. In a higher percentage, it is an inflammatory disease. The pinching is also accompanied by impaired hearing.
Inflammation of the middle ear
Otitis media is also known as otitis, otitis media or mesotheitis. It can be acute or chronic. It is subdivided into purulent inflammation or non-purulent inflammation.
The risk factor and sometimes the cause are upper respiratory tract infections or a reduced immune capacity of the body.
In upper respiratory tract infections, the virus or bacteria is transmitted through the Eustachian tube, but not infrequently through the blood. Another potential route for infection is through the perforated eardrum.
The most common causative agents include:
- respiratory syncytial virus RSV
- influenza A and B virus
- adenovirus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- staphylococcus aureus
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
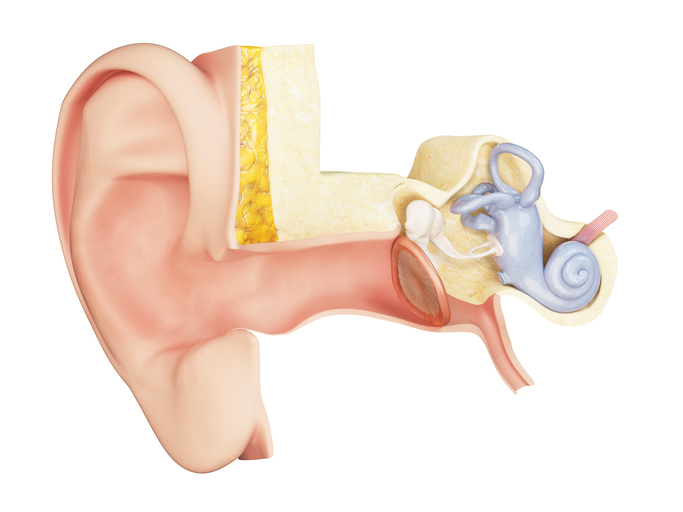
As written above, it accompanies upper respiratory tract infections. You are probably also familiar with the common cold caused by blowing a cold, known as a draught. It is also manifested by a pricking in the ear.
In most cases, only one ear is affected, rarely both. Bilateral inflammation is most common in young children.
It is a symptom of otitis media. It is a very common disease, especially in young children. The characteristic symptom is pain inside the ear, sometimes even discharge from the ear.
People with otitis media may also experience a sensation of lying down in the ear. Sometimes an elevated body temperature or fever is present. Also present is tinnitus, headache. In a small percentage of cases, vomiting may also occur.
The acute form has a rapid and sudden onset. In this case, the inflammation is usually bilateral. The chronic form is manifested more by itching and burning in the ear, sometimes even pressure. Of course, there is also a pricking in the ear.
The treatment of otitis media is mainly aimed at relieving the pain, but also at curing the inflammation itself. Paracentesis is performed and antibiotics are then given. This should prevent the inflammation from recurring in the short term in the future.
In addition, a prick in the ear is a symptom for ear canalitis. This is also a relatively common and painful ear disease. It is basically an inflammation of the external ear canal.
Inflammation of the ear canal and outer ear
It manifests itself mainly as ear pain, ear infections and subsequently impaired hearing. Sometimes there is discharge from the ear and increased body temperature.
Inflammation can occur, for example, as a result of a skin infection in the ear canal and ear. This can be of viral, bacterial or fungal origin.
Sometimes, however, the inflammation can also be caused by a blockage of the ear canal by sebum. In such a blocked ear canal, the infection is more easily established and also multiplies.
In this type of inflammation, there is not only a stinging sensation in the ear. It is also possible to distinguish otitis media from otitis externa by touch. In the case of an inflamed ear canal, the ear is sensitive to touch. This is also the case in inflammation of the cartilage of the external ear canal and ear.
For treatment, the ear needs to be cleaned and then ear drops, which have an antibiotic effect, should be applied. If the inflammation was caused by fungus, the doctor will also prescribe antifungals for the patient.
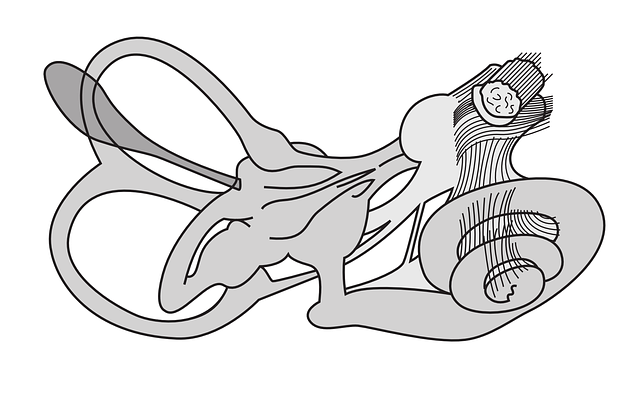
Inflammation of the inner ear
Labyrinthitis (inflammation of the labyrinth) is accompanied by pain, as well as nausea, vomiting and nystagmus (involuntary eye movements). The difficulty is exacerbated by head movements.
Transmitted pain to the ear
A twinge in the ear can also be caused by radiation from another location. This means that the epicentre of the pain is not in the ear. The pain arises in another location and is transferred to that area.
An example is pain in the teeth or gums due to various inflammatory diseases. Another possibility is the occurrence of the aforementioned problems after tooth extraction. Similarly, in the case of inflammation of the mucous membranes in the mouth, the pain can be transmitted to various areas, including the ear.
A separate category is inflammation of the processus mastoideus, which is actually part of the temporal bone. It is known professionally as mastoiditis. It is most often a complication of otitis media. It is also manifested by stinging in the ear.
Costen's syndrome is a disorder of the temporomandibular joint. One of its symptoms may be a pricking in the ear. This syndrome was described by James B. Costen, M.D., in 1934.
The primary neuralgia of the nervus glossopharyngeus (IXth cranial nerve, lingual nerve) should also be mentioned. Pain in the Vth cranial nerve (nerus trigeminus, trigeminal nerve) results in pain transmission and, for example, ear pricking.
People suffering from cervical spine pain are familiar with pain shooting into the head and pain radiating to the ear area (among other problems). Injury and foreign bodies are also among the possible causes of a prick in the ear. Therefore, a professional examination is recommended in case of problems.
Video on the causes of ear pain
Diseases with symptom "Pricking in the ear"
Interesting resources










