Wrinkles and skin aging: causes and effective help

Skin ageing is a process that cannot be stopped, but it can be slowed down to a certain extent. The first wrinkles appear around the age of 25 to 30. Do you know all the causes and factors of ageing? What really helps to reduce wrinkles?
Article content
Types of wrinkles, etiology of wrinkles, external and internal care, prevention of aging and many other interesting information can be found in the article.
Origin and type of wrinkles
Depending on our skin type, genetics, lifestyle and care, the first wrinkles appear individually between the ages of 25 and 30.
The first wrinkles that appear are mainly mimic wrinkles. These occur mainly around the mouth, eyes and forehead. Possibly a frown line between the eyebrows, but this depends on the individual facial expression.
Age lines are caused by both internal and external influences.
- Internal factors can include age, gender, genetics and the health of the individual.
- External influences may include skin care, lifestyle, exposure and protection from UV rays.
Collagen is an essential building protein in the human body. It is particularly important for musculoskeletal health (cartilage, muscles, tendons), skin (complexion), nails and hair quality.
Collagen slows down skin aging, wrinkle formation and improves healing after skin cover injuries.
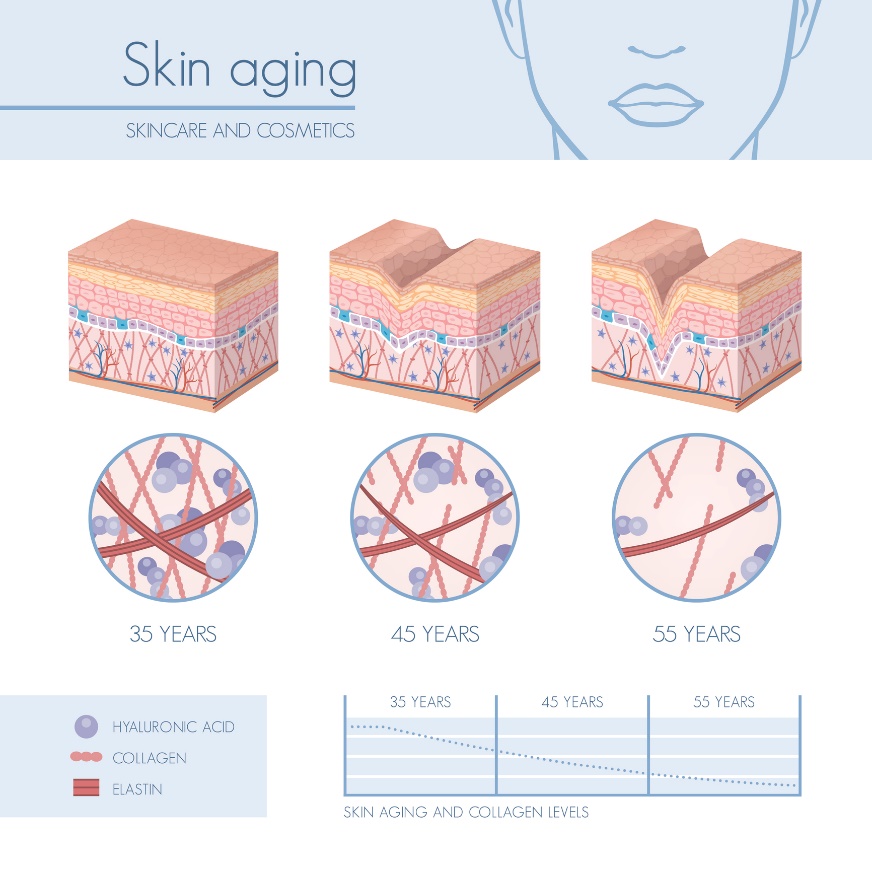
After the age of 25, collagen production decreases by approximately 1.5% per year, with almost no collagen production after the age of 40.
Protein synthesis of collagen, elastin and hyaluronic acid gradually decreases. This leads to wrinkles and skin ageing. Wrinkles can generally be classified according to type, depth or location.
Classification of wrinkles by type and age:
- Ageing stage around the age of 30 (mimic wrinkles)
- First wrinkles associated with mimicry and small changes in the skin support system
- Ageing stage around 40 years of age (elastic wrinkles)
- Change and degeneration of the supporting elastin fibres of the skin
- ageing stage around 50 years of age (atrophic wrinkles)
- Change and decrease in the amount of collagen fibres (atrophy)
- Ageing stage around 60 years (gravity, aphrotic wrinkles)
- Atrophy and degeneration of supporting skin fibres, collagen and elastin
Mimic wrinkles (dynamic)
Dynamic or mimic wrinkles are caused by the movement of facial muscles. They occur mainly in the forehead, around the mouth, eyebrows, eyes and neck. They are particularly visible during facial movement and mimicry.
They are conditioned by facial muscles that are fixed to the skin. Over time, they can become static wrinkles because the skin will no longer be able to contract back to its original state.
Examples:
- Horizontal forehead wrinkles (forehead wrinkling/lifting)
- Vertical wrinkles between the eyebrows (frown, frown)
- Fan-shaped wrinkles around the eyes (smiling, laughing)
- Wrinkles on nose and lips (laughing, talking, smoking)
Age lines (static)
Static or age lines are caused by time and are mainly related to the internal aging process of the body. The concentration of collagen, elastin, hydrolipids and hyaluronic acid in the skin decreases.
Gravity, which pulls the skin downwards, and external UV radiation also play a role. Last but not least, lifestyle, skin care and lifestyle factors (smoking, alcohol, stress, diet...) also play a role.
Static and dynamic wrinkles can be slightly more pronounced on one side of the face. This is a result of the slight natural asymmetry of the face and also of regular sleeping on a certain side.
Causes of wrinkles and risk factors
The aetiology of wrinkles is multifactorial. It can be divided into external and internal factors. Alternatively, it can be divided into controllable and uncontrollable factors.
Ageing itself is an irreversible process, as is gravity and the loss of collagen and elastin fibres. However, this process can be significantly slowed down by eliminating risk factors.
Internal factors
Intrinsic aging is a natural process that occurs over time and age regardless of external factors. This process is caused by the fact that after the age of 25, the human body produces 1% less collagen each year.
After menopause, or menopause, this decline is slightly more pronounced.
As in any other organ, the skin also undergoes an ageing process. Physiological ageing is approximately 30% genetically determined. Hormonal influences and age itself also play an important role.
There is a gradual loss of elastin, collagen, skin fat, thinning of the hydrolipidic layer and drying out of the skin.
In addition, the patient's health, medical history and possible diagnoses also play a role. Internal factors include internal nutrition, i.e. sufficient nutrients (especially proteins, vitamins and minerals).
External factors
Wrinkles are also caused by external factors. These include lifestyle, skin care, UV protection and the environment.
A diet with excessive sugar intake, lack of protein and insufficient drinking is not good for the skin. The body needs sufficient nutrients to nourish the organs, including the skin.
It has been shown that skin deterioration and facial wrinkles are more pronounced in smokers than in non-smokers. Alcohol is also a bad influence. Other external factors include, last but not least, chronic stress and insufficient regeneration of the body.
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation without a protective filter also contributes to skin ageing and wrinkles. UVA radiation affects the structures of the middle layer of the skin.
Ultraviolet radiation causes degradation of collagen fibres in the skin. Exposing the skin to sunlight accelerates the ageing process known as photoaging.
Lifestyle and the environment in which we live can accelerate the skin ageing process itself. Air pollution and extreme environmental conditions (chemicals, smog, harsh extreme weather...) are unsuitable.
Skin care is a category of its own. With sufficient hygiene, protection and nutrition, the aging process and the formation of wrinkles can be slowed down and to some extent mitigated.
How to eliminate wrinkles and aging?
While it is important to accept the fact that aging is a part of life, it is possible to slow down the process and eliminate it to some extent.
There are plenty of tips, advice and products on the internet that are supposed to counteract wrinkles. It can be difficult to navigate them as they may be marketing beauty products. The following are basic but proven and effective tips given by dermatologists.
Diet and drinking are essential
The quality and balance of your diet are extremely important for the functioning of all organs in the body, including the skin.
Although it may sound like a cliché, a poor diet low in protein, fat, vitamins and minerals does not provide the body with the tools to defend and regenerate tissues.
The foundation of healthy skin is a regular balanced diet full of nutrients, vitamins and protein. Hydration is important, not only from the outside but also from the inside, by drinking plenty of clean water.
On the other hand, excessive intake of simple refined sugar, alcohol and consumption of tobacco products is inappropriate.
Protection from the sun's UV rays
Protection from the sun's rays is a key factor in preventing photoaging. Skin doctors recommend daily use of sunscreen with an SPF factor against the sun's rays.
Human skin ages after chronic exposure to UV radiation. The texture and surface of the skin changes, thickening or thinning of skin texture, wrinkles, solar elastosis, collagen degeneration and pigment shifting appear.
Thus, a daily skin protection routine is important to maintain a youthful appearance and skin health. For temperate latitudes, a minimum of SPF 20 is recommended. In sunnier countries, protection of at least SPF 30 or higher is recommended.
Read also:
How to choose a sunscreen? Why SPF 50 for children and what is UV, SPF, phototype?
Skin care with appropriate cosmetics
Vitamin C is an essential ingredient for the synthesis (formation) of collagen. Vitamin A (retinol, retinoid) promotes the growth of new cells. It has anti-aging and anti-acne effects. Retinoids fight wrinkles and pigmentation. Vitamin E protects cell structures.
Your cosmetics can therefore contain vitamin A, vitamin C and vitamin E. Niacinamide and hyaluronic acid are also suitable. For dry skin, it is also advisable to reach for natural oils.
Extended care is also possible, for example, lymphatic facial massage, professional beauty treatments and so on.
The basis of healthy skin is sufficient hygiene in the form of thorough make-up removal and cleansing of impurities.
Due to differences in age, condition and skin type, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist about cosmetic products.
Does collagen supplementation help against ageing?
After taking collagen in the form of a dietary supplement, the body can break down the collagen protein and transport it to more "important" parts of the body than the skin.
A good example is the musculoskeletal system (cartilage, tendons), connective tissues of the body, vascular walls and more. If the body sends the collagen it receives to the skin, it should not be forgotten that the skin is the largest organ in the body. It weighs up to 10 kg.
Therefore, collagen supplementation in a dietary supplement may not lead to an increase in collagen in the skin to the extent that the marketing of nutritional products promises.
At present, studies have not shown that supplemented collagen has any negative effect on health. On the contrary, they report that taking collagen increases the total protein intake into the body.
Summary of anti-aging skin care and prevention tips:
- UV protection
- Complete balanced diet
- A healthy diet with plenty of vitamins and protein
- Adequate drinking of clean water
- Elimination of alcohol and smoking
- Elimination of daily stress
- Consistent hygiene, cleaning and make-up removal
- Quality and appropriate cosmetics with active ingredients
- Regular physical activity and blood circulation
- Elimination of expressive and repetitive facial expressions
Related










