- urologiepropraxi.cz - Testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men. MUDr. Otakar Štanc
- solen.cz - Testosterone supplementation - news, indications and safety. doc. MUDr. Juraj Fillo, PhD., MPH, MUDr. Michaela Levčíková
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - The many faces of testosterone. Jerald Bain
- ncbi.nlm.nih.gov - Physiology, Testosterone. George N. Nassar; Stephen W. Leslie.
What is the hormone testosterone and how does it affect the male body?

Testosterone is also known as the "male hormone". It is a male sex hormone that is largely represented in the male body. What is its role and importance in the human body?
Article content
Its production and secretion is controlled by the hormone of the subcortical gland of the adenohypophysis - luteinizing hormone LH.
The level of male sex hormones (androgens) begins to rise sharply at the onset of puberty. As a result, a more masculine male body type is formed, male genitalia and sexual desires are defined.
A sufficiently high level of testosterone is maintained until the age of 30-40 years of a man's life.
However, testosterone, considered the most important male sex hormone, is also found in low concentrations in women.
Testosterone, together with estrogen, plays a key role in the different appearance and behaviour of men and women. It thus creates sexual dimorphism.
Functions of testosterone in the body
A sufficient and balanced level of testosterone in the male body plays an important role already during the period of growth and puberty, when the development of primary and secondary sexual characteristics - muscle mass, pubic hair growth, voice mutation, male body proportions, etc.
The most important function of testosterone is the stimulation of sperm production in the testes - spermatogenesis.
The main function of testosterone in a man:
- Development of male sexual characteristics
- Stimulation of spermatogenesis (sperm production)
- Fertility and sperm quality
- Effect on libido and sexual behavior
- Erectile activity
- Development of muscle mass
- Regulation of energy metabolism
- Effect on energy and performance
- Dominant character
- Effect on mental state and mood
The upper normal limit of testosterone levels is considered to be 1000 to 1200 nanograms per deciliter.
The lower limit is set at 300 nanograms per deciliter.
Testosterone production in the male body does not proceed uniformly throughout life. After a sharp increase in testosterone production at puberty, androgen production slowly stabilizes during working age.
Individually, depending on the lifestyle and health of the man, already from 30-40 years of age, the production of androgens gradually decreases.
The most significant decrease in testosterone occurs after the fiftieth year of a man's life. This manifestation is called the period of andropause - the syndrome of the aging man.
Andropause is a period of male transition associated with a decrease in the formation and level of androgen hormones. Symptoms of andropause come all gradually and gradually.
Possible symptoms of andropause:
- Decrease in libido and sexual desire
- decrease in energy and performance
- deterioration in sleep quality
- mood changes, anxiety, depression
- impaired memory and concentration
- erectile dysfunction
- impaired erection and achievement of orgasm
- decrease in muscle mass
- increase in fat reserves
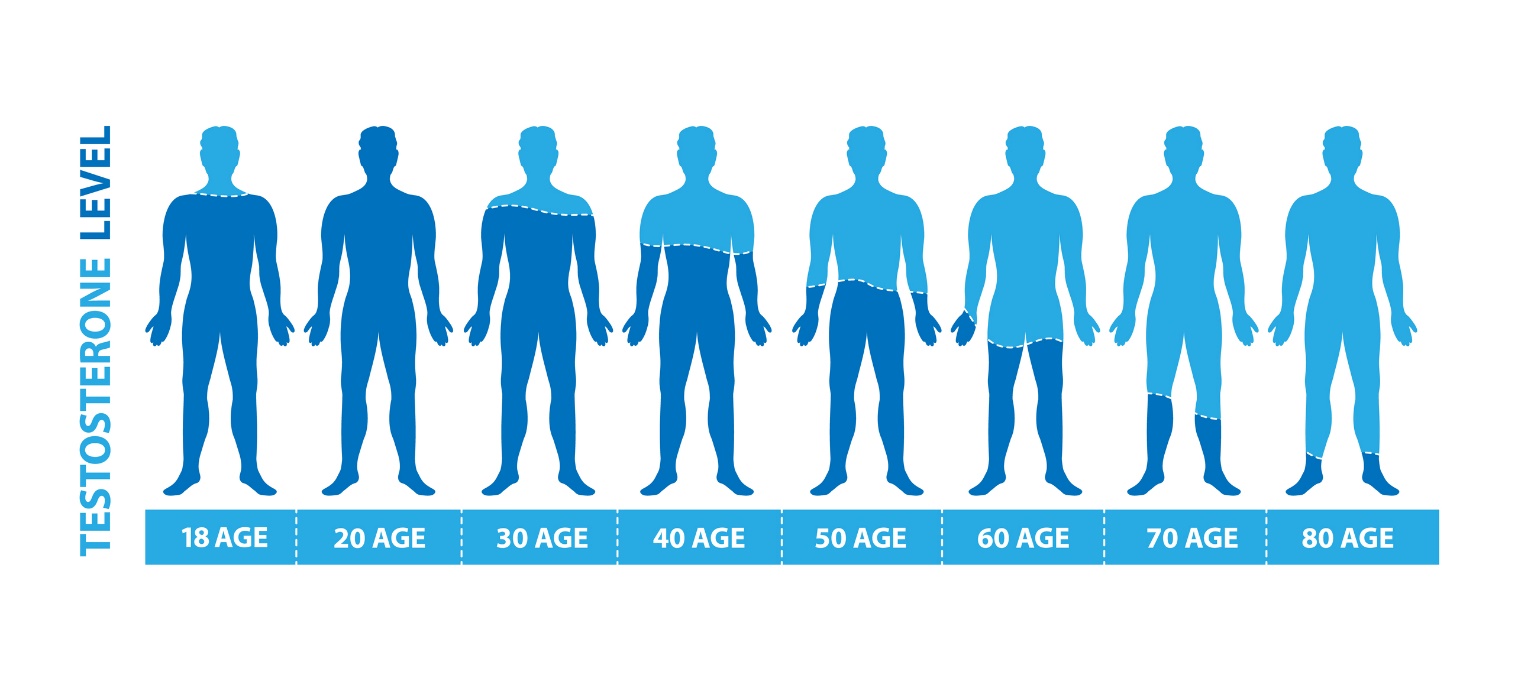
Loss of testosterone
Loss of the hormone testosterone can occur naturally as you age, but low testosterone levels can also occur at a younger age.
Hormone levels are affected by age, lifestyle, diet, physical activity, health and hormonal system.
Reduced testosterone levels can be the result of a disorder of the hormonal system in the sense of a problem with the production of gonadotropic hormones, a disorder of the thyroid gland, adenohypophysis in the brain, a tumor, a disorder of secretion directly in the testicles or a side effect of drug therapy.
A negative effect on testosterone levels is due to poor lifestyle factors such as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and unhealthy eating habits.
Foods with too much natural estrogen (soy products) are also a problem. Long-term stress, lack of sleep, poor recovery and especially lack of physical activity have a major impact on testosterone levels.
The most common symptoms of testosterone decline
- Low sexual desire
- Erectile dysfunction
- Fertility problems
- Gynecomastia (breast enlargement)
- Mental instability
- Hypersensitivity
- Increased fatigue and exhaustion
- Problems of the cardiovascular system
How to increase testosterone levels?
Treatment of low testosterone levels can be addressed with hormone replacement or natural remedies. When testosterone levels drop, it is necessary to identify the cause and then determine the appropriate type of therapy. Therefore, consultation with a doctor is recommended.
Hormonal treatment
Hormone replacement therapy is tied to a doctor's prescription. Testosterone-containing preparations (tablets, injections, patches, gels) will increase the level of testosterone to its physiological level.
However, changes to the body may only become apparent after several months of treatment.
Hormone replacement therapy with testosterone is a long-term treatment. It is therefore important that it is safe and effective with respect to the patient's health.
Currently, oral tablets, injections, skin gels and patches are available as part of hormone replacement therapy.
In the initial phase of treatment, short-term preparations are preferred because they can be discontinued quickly in the event of possible side effects.
The best results are achieved with three-monthly injections of testosterone replacement. Men receive 4 injections over the course of a year. The injectable preparation is not metabolised in the liver and so there is often no need to monitor liver parameters.
Natural treatment
The natural form of treatment consists of an appropriate diet with emphasis on supplementation of magnesium, zinc, selenium and vitamins B, C and D.
Eggs, avocados, almonds, beef, coconut or olive oil and other forms of healthy fats should be included in the diet.
However, beware of increased intake of soy products, which contain phytoestrogens - the natural form of dietary estrogens.
Alcohol and caffeine intake and smoking should be limited.
A suitable way of stimulating testosterone is exercise and movement. Strength training positively helps to flush out testosterone, especially in the case of short-term and high-intensity training.
An important role is played by quality sleep and sufficient recovery.
Adequate hardening is recommended, as cooling the testicles stimulates testosterone production. However, this form of therapy should be consulted with a doctor.
Over-the-counter preparations (testosterone tablets)
Dietary supplements in the form of tablets containing natural substances and medicinal herbs are suitable for the overall support of testosterone production. These are supportive agents that can be purchased without a prescription.
Examples are ground anchor (Tribulus Terrestris), true ginseng, fenugreek, saw palmetto or maca.
Anchovy is a popular herb especially for its high content of anabolic steroids of plant origin. The plant is called the "green viagra" for its positive effect on libido and sex life.
Beware of synthetic preparations and anabolic steroids, which have a large number of undesirable physical and psychological effects on the human body.
Possible side effects of anabolics:
- higher risk of cancer (prostate, liver)
- higher risk of heart attack
- kidney damage
- negative effects on the psyche
- acne
- hair loss
- addiction

Excess testosterone
A significant excess of testosterone in the body is not healthy. High levels of this hormone can manifest as moodiness, aggression, risky behavior, high blood pressure, excessively increased libido, acne, extensive body hair and baldness.
It can be caused by hormonal disorders, thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, cancer, anabolic steroid use, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and a significantly unhealthy lifestyle.
Treatment consists of finding the cause and balancing the level of male hormones to a natural level. Therefore, a consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Testosterone levels in women
Women have approximately 7 times lower levels of testosterone in the body than men. In women, the standard level ranges from 15 to 70 nanograms per deciliter of blood.
If testosterone levels fall below 15 ng/dl of blood, women may experience problems getting pregnant, decreased libido and sex drive, irregular menstrual periods, and changes in breast tissue.
If testosterone levels exceed 70 ng/dl of blood, women may experience weight gain, muscle growth, higher blood sugar, missed menstrual periods, aggressiveness, acne, and increased pubic hair growth.
Testosterone in women may begin to rise with, for example, hormonal disorders, excessive iodine intake, anabolic steroid use, hirsutism, PCOS, and other disorders.
In both cases, it is a hormonal imbalance. To determine the cause and determine the type of treatment, a professional consultation with a doctor is necessary.
Interesting resources










