- escardio.org - 2018 ESC/ESH Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension
- heart.org - Blood Pressure Fact Sheets
- vusch.sk - Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- npz.sk - Hypertension.
FACT: What blood pressure readings are normal, what is a little and what is a lot?

Blood pressure readings often give us a headache. Literally. What's too little and what's too much?
Article content
- 1. Blood pressure values in numbers
- 2. ✔✔ OPTIMAL blood pressure
- 3. ☑ NORMAL blood pressure
- 4. ↑✔Higher normal blood pressure
- 5. ↑ HIGH blood pressure of the 1st degree
- 6. ↑ ↑ HIGH blood pressure grade 2
- 7. ↑↑↑ HIGH blood pressure grade 3
- 8. ↑↑↑↑ HIGH blood pressure grade 4 - hypertensive crisis
- 9. ↓ LOW blood pressure
- 10. In the USA, the rules are stricter
- 11. First value / second value
- 12. Some risk factors leading to hypertension
Neither too low nor too high is appropriate. Optimal is if we have its values somewhere in the middle.
Each of us is, of course, an individual.
Young girls and women, for example, have a predisposition to lower pressure. On the one hand, this protects them from cardiovascular complications. The disadvantage is the drop, which leads to a horizontal position. The cause is reduced blood supply to the tissues and therefore to the brain.
Surely you have heard that the disease called arterial hypertension does not hurt (...and that's until it starts to hurt). Believe me, you would not want to experience the problems that occur at pressure altitudes.
When the pressure rises, your head gets dizzy and so does your whole body. After all, the silent killer isn't called by that fateful name for nothing. Prolonged exposure to hypertension is harmful.
Hypertension increases the risk of cardiovascular complications and diseases such as atherosclerosis, heart disease (heart attack, IHD, heart failure), stroke, kidney disease, visual impairment and more.
When is it necessary to check it?
1. Blood pressure values in numbers
What is the norm? What is too low? What is too much?
Blood pressure = pressure in mmHg
2. ✔✔ OPTIMAL blood pressure
Pressure less than 120 / less than 80
Reduce cardiovascular risk and disease.
3. ☑ NORMAL blood pressure
TK 120-129 / 80-84
4. ↑✔Higher normal blood pressure
TK 130-139 / 85-89
Professional examination and blood pressure control is required from the moment a person repeatedly measures values in this range and higher.
The risk of cardiovascular disease is increased.
5. ↑ HIGH blood pressure of the 1st degree
TK 140-159 / 90-99
6. ↑ ↑ HIGH blood pressure grade 2
TK 160-179 / 100-109
7. ↑↑↑ HIGH blood pressure grade 3
Pressure 180 and above / 110 and above
+ Some publications also list 4th degree.
8. ↑↑↑↑ HIGH blood pressure grade 4 - hypertensive crisis
Pressure 210 and above / 120 and above
9. ↓ LOW blood pressure
Pressure less than 90 / 60 and below
A pressure check and professional examination is necessary if a person is having problems and his/her pressure falls below these values. BUT some people have a pressure in this range for a long time and even without experiencing difficulties.
These blood pressure values are given by the European Society of Cardiology, also in Slovakia.
10. In the USA, the rules are stricter
In the United States, the values are more strictly looked at.
Blood pressure values according to the American Heart Association:
- NORMAL 120 and below / 80 and below
- Elevated 120-129 / 80 and below
- Grade 1 hypertension 130-139 / 80-89
- Grade 2 hypertension greater than 140 / 90 and above
- Hypertensive crisis more than 180 / more than 120
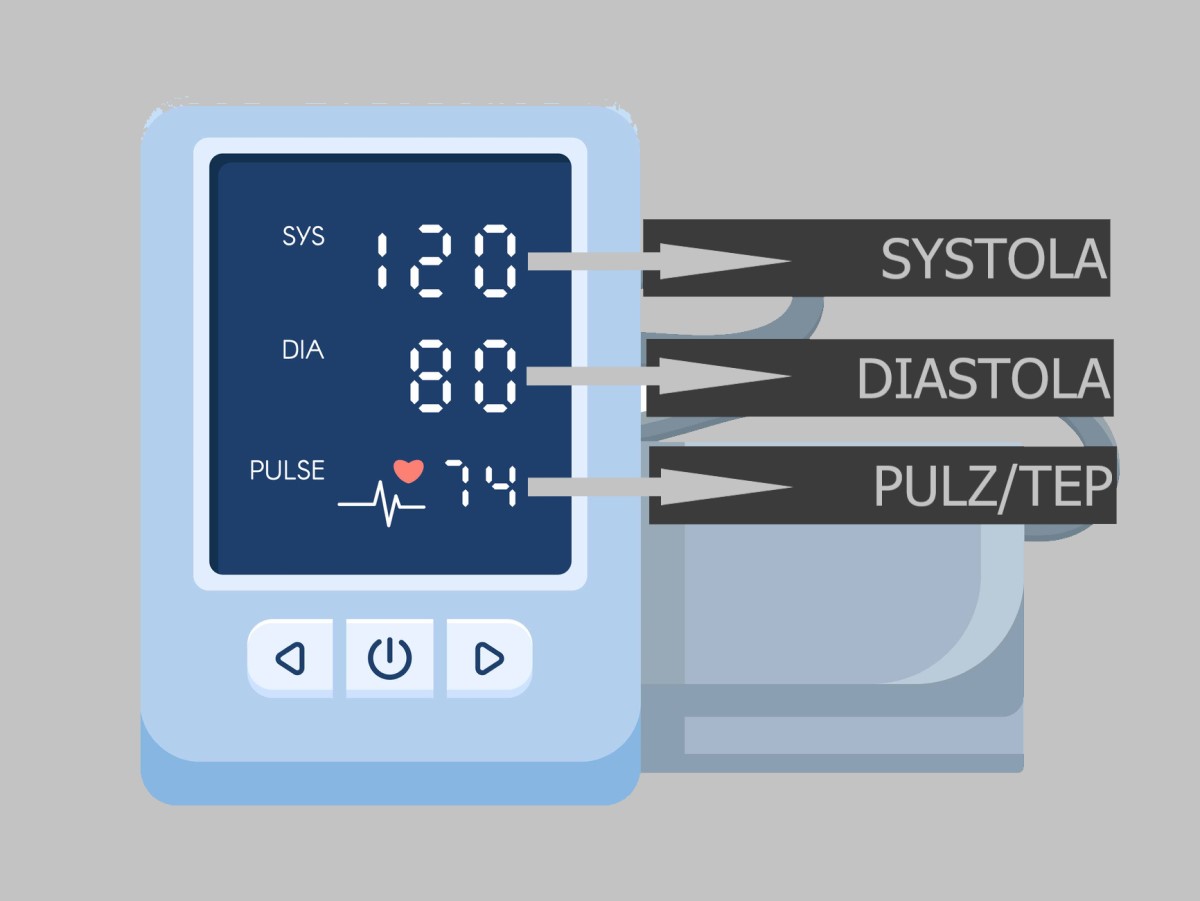
11. First value / second value
For a quick recap...
When measuring, two values are always given (table)
| Upper blood pressure value | Slash | Lower blood pressure |
| Systola | / | Diastola |
| 120 | / | 80 |
| Upper blood pressure | displayed on the blood pressure monitor | Lower blood pressure reading Often referred to as heart pressure |
| Blood pressure during systole, the ejection of blood into the circulation | / | Blood pressure during diastole, when the heart is weakening |
| Systolic blood pressure | Diastolic blood pressure | |
| The value is given in millimetres of mercury = mmHg | ||
12. Some risk factors leading to hypertension
Some factors we can and others we cannot control by our actions:
- Smoking, passive smoking
- diabetes
- overweight and obesity
- high cholesterol
- high salt/sodium intake
- unhealthy and unbalanced diet
- insufficient fluid intake
- alcohol and excessive intake
- insufficient physical activity
- family history, heredity and genetic predispositions
- age
- male/female gender
- early menopause
- hypertension in pregnancy, pre-eclampsia
- thyroid disease
- kidney disease
- autoimmune and inflammatory diseases
- sleep apnoea, snoring, sleep disorders
- stress
- socio-economic-psychological status
- ethnic and racial origin
- environment
View Full Article : Summary table - What are the values of low, normal and high blood pressure?
+ Cardiovascular (heart) disease category + How to have a healthy heart and blood vessels
+ Diseases:
Interesting resources










