- webnoviny.sk - What about hemorrhoids? You can get rid of both internal and external ones, but not always without the help of the doctor
- solen.sk - Risk factors for the development of hemorrhoids and remission of their manifestations after the application of a multicomponent medical device
- chirurgia.name - Surgical treatment of hemorrhoids
- oschir.jfmed.uniba.sk - about the disease
- nspskalica.sk - professional article
- wikiskripta.eu - on Wikiscript
- encyklopedia.akv.sk
- nemocnicakomarno.agel.sk
Hemorrhoids, Golden Veins: What Are The Symptoms And Their Treatment? (external, internal)

Hemorrhoids or as know also as piles, are a frequent problem of adults with a significant impact on comfort and often even ones' psyche.
Most common symptoms
Characteristics
Hemorrhoids are clusters of blood vessels that occur in humans under normal non-disease conditions. However, the disease form is caused by the dilation of the plaque of vessels that occurs in the area of the anal canal and anus.
From the Latin nodus haemorrhoidalis,
from gr. haemorides flebes,
haimorrhoides / haima, heama = blood and rhoos = flowing.
Varem haemorrhoidales.
The golden veins, or hemorrhoids as colloquially called, are the result of a combination of several factors. Consequently, they negatively affect the vessels in the rectal and anal area.
Similar to varicose veins of the lower extremities, although in this case varicose veins in the rectum.
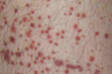
The final manifestation is unpleasant difficulties, which in addition to itching or pain in the rectum include occasional bleeding along with stool or blood on toilet paper.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are hemorrhoids?
What do they look like and what are their symptoms?
How are internal and external hemorrhoids treated?
What is effective in removing them and do grandma's recipes help?
In short, it is a disease of the vascular supply in the rectum, anal canal, and anus (anus - circle).
They are located in the final area of the anal canal, which is the stretch of at last 3 centimeters of the rectum.
As already mentioned, this vascular tangle, ie the hemorrhoidal plexus, is in this area even under normal conditions.
The rich plait of arteries, veins, and capillaries, along with connective tissue and smooth muscle, form soft spongy structures that line the perimeter of the anal canal.
They are commonly described in the literature as pads. Their job is to keep the anus closed and hold the stool.
How can we control stool emptying? In addition, an important function is the perception of a feeling of fullness and pressure on the rectum, the anal canal.
Plus...
In addition to controlling stool retention and defecation, important role plays also:
- anal channel sealing
- maintaining the cleanliness of the anal area and anus
- mucosa and skin section (dentea linea)
So what are the hemorrhoids?
These are dilated vessels that line the end section of the anal canal before its opening, i.e. the anus, its part, and also behind it.
They affect a large percentage of people over the age of 40 (sometimes even younger). It is estimated that after 50s, over 50% of people suffer from it. They affect women and men to about the same extent. However, very often they accompany pregnant women and mothers.
Rectum, anus, and vessels
The rectum is the final section of the large intestine. It is about 12 centimeters long and about 4 cm thick. It consists of the transverse lashes of the rectal mucosa, with the last part before the anus being the ampoule of the rectum.
In the area, there is the upper hemorrhoidal plexus, ie the vascular girdle, and thus the rectal veins - venae rectales superiores et inferiores .
This area does not have sufficient innervation and is therefore not sensitive to pain.
Before the rectum opens into the anal opening, there are two clamps in the anal canal.
The rectum is terminated by an anal opening and its surface is made of squamous epithelium, so the skin covering is sensitive to pain.
In addition, there are rich blood tangles in this area and their complex is referred to as the lower hemorrhoidal plexus. It is formed by the anal vessels of the venae analis.
Hemorrhoids are divided according to their location into external and internal :
- internal
- external
The table lists the main features of internal and external hemorrhoids
| Internal |
|
| External |
|
| Internal and external hemorrhoids often occur together in a combined form as mixed hemorrhoids | |
The golden vein is often asymptomatic until it progresses to a higher stage. It is generally known for blood in stool, bleeding, and blood on toilet paper, along with itching of the anal area. However, there can be more accompanying difficulties.
These health problems are often the result of deteriorating comfort and mental stress. In addition, people are often ashamed to deal with it due to its intimate nature.
At the same time, nowadays their treatment, even at a higher stage, is undemanding and mostly uncomplicated.
Of course, it is important to note that bleeding, as well as the other problems, can be accompanied by other diseases of the digestive system, from minor functional problems to inflammatory or serious oncological diseases. Therefore, if they occur, it is important to have a professional examination followed by adequate treatment.
You might ask:
What causes hemorrhoids?
Causes
The cause is the dilation of the vascular plexus in the area of the anal canal and anal opening.
The main impact on the bulging of the blood vessels is their increased filling and insufficient blood flow. Together, they help to weaken the lining of the vascular wall and connective tissue.
+ present might be...
Interaction of several factors, ie multifactorial action, in which genetic predispositions participate, weakening of the vascular wall and the increase of pressure in the small pelvis.
Risk factors for the formation of a golden vein:
- genetic predisposition and familial occurrence
- hereditary, ie hereditary risk of occurrence of up to 42%
- increased filling of blood vessels, veins, and insufficient drainage
- weakening of the ligament and vascular wall
- increased tone - the pressure of anal sphincters, which worsens blood flow
- older age, especially over 50 years
- malnutrition
- increased intra-abdominal pressure
- pregnancy and childbirth
- diseases of the small pelvis, inflammation, tumors, ascites
- long-term cough
- pelvic floor disorders
- eating habits, low fiber, spicy foods, food quality
- lack of fluids
- bad defecation habits
- long sitting on the toilet
- long-term strenuous defecation with vigorous pressure on the stool
- frequent constipation and diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome
- sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work and lack of exercise
- long standing position
- obesity
- cold, sitting in the cold
- mechanical irritation of the rectum, an example is anal intercourse
- alcohol - alcoholism
- smoking
- stress and psychological factors
Important factors are poor lifestyle, sedentary lifestyle, poor defecation habits and low fiber in the diet.
Possible incidence of complications. These include vascular thrombosis, which causes pain and bleeding, but also the aforementioned prolapse, ie the fall of varix through the anus.
Prolapse is risky especially from the point of view of strangulation of collapsed structures, which in turn causes other health problems.
Warning!
Sitting in the toilet is significantly negative.
It is one of the risk factors for the development of hemorrhoids and thus
directly affects the its development.
The most natural and best position to empty the stool is squatting.
Sitting-style toilets are typical of Western cultures, and it is in this population
that the incidence of hemorrhoids is increased.
Hemorrhoids experienced during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is an important factor in the development of hemorrhoids. The cause is not only hormonal changes but especially an increase in pressure in the pelvis and abdomen.
Of course, weight gain also affects it, and that not only from the mother's point of view but also from the fetus. The larger it is, the more it affects the conditions in the abdominal cavity.
Read also:
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy and after childbirth: Why do they occur, how to treat them?
Wondering if the golden vein disappears by itself after giving birth?
Yes, it happens.
After childbirth, usually, the golden veins disappear by itself. Even without the need for major professional intervention or the need for invasive, surgical treatment.
However, it depends on the condition of the vascular system before pregnancy and before childbirth.
The removal of hemorrhoids can thus be expected within a few days to weeks.
Symptoms
The symptoms are well known, mainly bleeding during stool and blood on toilet paper .
The trigger is hard stooling and excessive pressure on the stool. Possibly frequent and rare diarrhea.
The blood, on the other hand can be light and bright red to dark.
Blood may be present on the surface of the stool, or it may be dripping into the toilet during defecation. It is usually smaller, but it can also be larger.
It is typically on toilet paper when cleaning the anus after defecation
Stages 1 and 2 have an asymptomatic course. Possibly with occasional bleeding.
The pain may not be present at all. And this applies to internal hemorrhoids. And it occurs only in the later 3rd - 4th stage of the disease.
Vice versa ...
External hemorrhoids are characterized by pain that stems from skin irritation and frequent inflammation.
The skin around the anus is convex, it contains small blue nodules. They do not have to hurt until the mentioned inflammation.
Symptom Summary :
- discomfort in the area of the anus
- itching of the rectum, anus, and its surroundings
- a feeling of pressure and tension in the rectum
- pain, especially inflammation and skin irritation, and persistent prolapse of internal hemorrhoids
- bleeding, blood on toilet paper
- rectal discharge - mucus secretion
- stool outlet for leaking and soiling of underwear with stool
- the output of the golden vein when pushing
- swelling in the rectal area
- redness to a crack in the anus, fissure or
- traffic jam
As already mentioned, the complications are thrombosis, ie the formation of blood clots in the varices, ulceration of damaged bloodless tissues with necrosis and severe pain, and spotting even without stool and bowel incontinence (inability to hold it).
One possible complication may also be the release of a blood clot and thrombus embolism into another part of the bloodstream.
You ask:
Can hemorrhoid bleeding endanger health and life?
In the vast majority of cases, this type of bleeding does not cause anemia and is therefore not so serious as to endanger human health and life. However, rarely and for associated problems, this is not completely ruled out.
Interesting information in the article:
Do I have hemorrhoids? What are hemorrhoids, their causes, symptoms and treatment
Diagnostics
Diagnosis has a medical history as a basis. The person complains of bleeding, itching, pressure, painful bowel, and pain in rectal area.
This is followed by a physical examination, on the left side, on the four limbs (genupectoral position), or on the back with bent and outstretched legs, both by sight and examination per rectum, ie by a finger over the rectum.
Visual examination of the rectum and anus with aspexia, palpation.
This is followed by anoscopy, rectoscopy to sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, also to rule out other bleeding and diseases of the digestive system.
In addition, abdominal X-rays, SONO or CT or MRI are added.
This, together with laboratory blood tests for blood counts (hemoglobin, hematocrit) and others, such as coagulation, especially when taking blood medicines.
Of course, there is also examination of the stool, as an example is a round, hidden bleeding.
You ask:
When is it necessary to see a doctor?
When there is bleeding in the stool,
with itching and pain in the rectum.
Table: Determine the presence of risk factors
| Symptom | The presence |
|---|---|
| Rectal pain | Frequent |
| Stool with blood and bleeding | Quite common |
| Itching of the rectum | Often |
| Stool pain | Often |
| Lifestyle and health style | Risk level |
| Sedentary work | High risk |
| Low fiber in food and solid diet | Fewer risks |
Did you find to have more symptoms and risk factors present? You should see a doctor for an examination, as it might be a sign of the high risk of hemorrhoids.
Wondering who treats hemorrhoids?- A surgeon or a proctologist.
Proctology = the science of rectal diseases.
Course
The course depends on the form of the disease. Internal ones are often asymptomatic . Bleeding occasionally occurs. However, this happens mainly in stage 1 hemorrhoids.
In stage 2. there is already a prolapse of dilated veins and tissues when you put pressure on your anal or rectal area. Following it, they retract by themselves.
Stage 3 is characterized by a prolapse remission disorder. However, it can be pushed in manually with the finger.
In the 4th it is no longer possible to manually correct this failure.
At this point, other difficulties are already associated, which results from the state of clotted blood vessels and tissue in the rectal opening.
Non-bleeding, formation of thrombosis, blood clots, and subsequent death of structures are accompanied by unpleasant and intense pain.
Large hemorrhoids are a source of other problems.
First, an anatomical disorder of the anus is causing a leak. As a result, soiling of the underwear to stool incontinence is present.
This is where the problem of skin cleanliness and fecal irritation begins. Irritated skin, inflammation, and susceptibility to damage to the skin cover, ie rupture of the anus or perianal abscess (purulent deposit near the anus).
The problem is similar to external hemorrhoids. However, these alone are rare.
Typically, people complain of uncomfortability, discomfort and tension in the anus, unpleasant itching, and even pain. Together with skin irritation and inflammation.
In most cases, the internal ones are accompanied by external hemorrhoids, and thus together as a mixed form.
How long do the difficulties last?
Swelling, irritation, and redness last for several weeks. Pain for several days.
Bleeding may have the following characteristics:
- bright red blood, but may also be darker, from a ruptured sac, with thrombosis present - thrombotic hemorrhoid, filled with blood
- on the stool surface - hematochezia
- on toilet paper
- drips down the stool into the toilet from the anus
- blood with mucus
Thrombosis, i.e. the formation of a blood clot for a circulatory disorder, is a barrier to drainage. This significantly increases the volume of the varicose vein. One can feel the lump.
At this stage, there is also a rupture of the filled cam, with bleeding present. What may be an indication for surgery?
You ask: Hemorrhoids and cancer risk relation?
Hemorrhoids certainly do not cause cancer. However, chronic mucosal and skin irritation, persistent inflammation, and mechanical irritation are negative predisposing factors.
Complications resulting from hemorrhoids:
- thrombosis, blood clot formation, and there is a risk of loosening and thromboembolism
- The hemorrhoid is shaped and sized like a cherry with a darker color, down to purple
- also with swelling in the area of the anus
- prolapse
- stool retention disorders
- bacterial infection
- crack or crack
- abscess - a sac filled with pus
- fistula - canal
- bleeding, rarely major blood loss
- anemia - less often
- zápcha
- increased body temperature
How it is treated: hemorrhoids
Interesting resources