- James WD, Elston DM, Berger TG, Andrews GC, et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. pp. 308–311. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- "Vaginal Candidiasis". Fungal Diseases. United States: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- "Candida infections of the mouth, throat, and esophagus". Fungal Diseases. United States: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 13 November 2019. Retrieved 24 Dec 2019.
- "Candidiasis". Fungal Diseases. United States: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
- "Treatment & Outcomes of Oral Candidiasis". cdc.gov.
- "Oral Candidiasis Statistics". cdc.gov.
- "Genital / vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC)". cdc.gov.
- "Symptoms of Oral Candidiasis". cdc.gov.
- "Thrush in men and women". nhs.uk. 9 January 2018.
- "Symptoms of Genital / Vulvovaginal Candidiasis". cdc.gov.
- "Symptoms of Invasive Candidiasis". cdc.gov.
- "Candidiasis". cdc.gov. February 13, 2014.
- Walker M (2008). "Conquering common breast-feeding problems". The Journal of Perinatal & Neonatal Nursing. 22 (4): 267–74.
- "People at Risk for Genital / Vulvovaginal Candidiasis". cdc.gov.
Aphthae: What is their cause and are they contagious? + What will help in treatment?

Aphthae are classified as inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. They affect every fifth person. Most often children and young adults. The exact cause of the disease is still unknown. In most cases, they are mild and disappear spontaneously within 10 days.
Most common symptoms
- Aphthae
- White tongue
- Fever
- Increased body temperature
- Scars
- Indigestion
- The Island
- Malnutrition
- Concentration disorders
- Blisters
- Buds
Characteristics
The ulcer, ulceration, affects only minimally below the level of healthy mucosa.
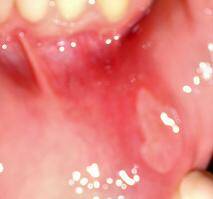
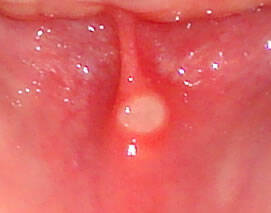
The color of aphthae is first yellowish, then white to gray. After rupture, the ulcer is sharply demarcated and there is redness behind the rim. This red hem is also technically referred to as an erymatous halo hem .
Aphthous inflammation can be alone or accompanied by ulcers, and they also occur in numbers. They have an oval shape, a circle.
Aphthae is one of the most common problems in the oral cavity.
In the past, they were also mentioned by the Greeks.
The disease affects 20% of the population, or about every 5th person.
They are characterized by pain that is exacerbated by irritation. Such as when eating, drinking or talking.
Aphthae are divided into three main groups :
- small aphthae , professionally also minor, stomatitis aphtosa minor or Mikulicz ulcers
- large aphthae , major or even stomatitis aphtosa major, or Sutton's ulcers
- herpetiform types
The table shows the distribution and description of aphthous inflammations
| Kind of | Small aphthae | Large aphthae | Herpetiform aphthae |
| Size | up to 4 mm | on average 1 cm rarely also size 3 cm |
smaller ulcers resemble herpetic inflammation |
| Count | up to 6 pieces | up to 6 pieces | even up to 100 ulcers |
| Frequency | most often 80% | about 10% | up to 10% |
| Age and gender | childhood, adulthood | childhood, adulthood | young adults and, in most cases, women |
| The place | lips buccal mucosa mouth of the mouth soft climate less often: gums and upper tongue or his back, dorsum |
anywhere most common: lips tongue buccal mucosa soft climate | most often the language of its lower area |
| Length | within 10 days | about a month | about a month |
| Intensity of difficulties | mild minimal difficulty | higher intensity can leave scars often recur - they recur |
intense painful ulcers often merge resembling herpes, but no viral infection is present |
Small aphthae are therefore smaller ulcers, up to 4 mm in size. Their number is up to a maximum of 6 pieces and the course is moderate. They often expire spontaneously within 10 days.
Large aphthae are usually 1 cm in size, however, up to 3 centimeters. Their number is also smaller. The course is already more intense. And it heals for about a month.
Although herpetiform aphthae resemble herpes infection in appearance, they have not been shown to be infected with the herpes virus. Their course is of the highest intensity.
If there is only one aphthous ulcer , no professional examination is necessary. However, the situation changes as more of them occur and the difficulties recur .
Then diagnosis and investigation of the cause is important . Especially for the herpetiform species.
Causes
They mostly affect young people, children and adolescents. However, they occur at any age.
The cause is not fully understood, but it is assumed:
- genetic predisposition
- associated with HLA antigens
- a third of those affected will have a familial occurrence
- lack of
- Vitamin B12, B6 and B9 (folic acid)
- iron
- related to conditions and diseases such as:
- celiac disease
- Crohn's disease
- other gastrointestinal disorders
- irritable bowel syndrome
- IBD - inflammatory bowel disease
- gastritis
- peptic ulcer disease
- allergy to certain foods
- pernicious anemia
- reduced immunity
- hormonal changes in women in connection with the menstrual cycle, pregnancy
- smoking and in particular the period after the habit
- stress
- and condition after injuries
- bad teeth cleaning technique
- bite of the inner mucosa of the cheeks or lips
- ill-fitting toothpick
- after injection in a dentist
Symptoms
After the rupture of the membrane, ie the membrane, an ulcer is formed , ie ulceration. This only extends to a minimum depth. However, deep damage is greater in the herpetiform form.
The ulcer is bordered by a sharp border , which is referred to as an erymatous halo border .
Ulceration arises in one , separate, but also as more numerous groups . These do not merge in most cases. This only happens in the case of a herpetiform species.
Small aphthae up to 4 mm and large, mostly 1 cm in size, however, can also occur in dimensions of 3 centimeters. Small ones usually disappear within 10 days. The others even within a month. In large and herpetiform cases, a scar may form after healing.
You ask: Are aphthae in the mouth portable or not?
Answer: No, they are not an infectious disease, so they are not transmitted from person to person, child to child.
What difficulties accompany aphthae?
We briefly list the most common difficulties accompanying the formation and occurrence of aphthae:
- pain
- it is exacerbated by irritation when eating, drinking, talking
- pain at rest is less common
- it is aggravated by sour, salty or spicy food
- before the blister is formed, it is possible to feel the tension or burning of the place
- swelling
- touch sensitivity
- redness around
Where do aphthae most often form?
Aphthae affect the oral cavity, its mucous membranes, as well as the lips or tongue.
Small aphthae are preferentially formed in places such as the mucous membranes of the lips, cheeks, base of the mouth, ie the place under the tongue, but also in soft climates. They do not form in the harsh climate. The tongue, and therefore its upper part, which is referred to as the dorsum (back) is rarer.
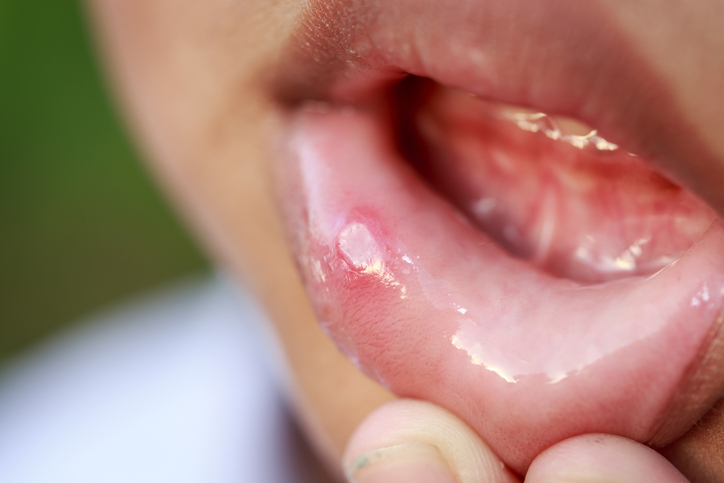
Large aphthae can form anywhere. However, most often on the lips, tongue, buccal mucosa and soft climate. Or even in the throat.
Buccal mucosa = professional mucosa cheek = cheek mucosa
Herpetiform aphthae most often affect the lower part of the tongue.
You ask - I have aphthae, aphthae?
You have probably found:
- small and whitish or yellowish ulcer
- in most cases it has a red edging
- clearly demarcated
- size varies:
- from smaller ones with a diameter of half a centimeter
- up to larger aphthae, which reach two to three centimeters
- appears mostly on:
- climate
- inside the lips
- language
- on the inside of the facial mucosa in the oral cavity
- unpleasant pain at the site of aphthae occurs even a few days (usually 1-3) before its actual occurrence
- the place is whiter from the beginning
- aphthae, which is clearly demarcated
- it is painful to the touch
- the boundary is slightly raised in height
- the center of the aphthae is lowered
- in most cases they do not appear in large numbers
- sometimes they can be sown and then the disease is very unpleasant and complicated
- larger aphthae also cause pain when chewing food, drinking or ordinary speech
- sometimes they can also cause fever
- Aphthae in the mouth in young children can cause food rejection due to pain
Diagnostics
So what we see is seen by the doctor. Alternatively, we first feel the tongue in our mouths.
Aphthae, which occurred on its own and disappeared within 10 days, does not recur, it does not need to be examined by a specialist. However, the situation changes with different behavior.
In many cases, aphthae occur in chronological order, one disappears and the other forms. Also, if their number is higher and the course is complicated by infection with microorganisms.
Alternatively, in the case of the herpetiform form. Or if you're not sure it's an aphthae.
We can also confuse them with another disease that affects the mouth and oral cavity.
The most common causes of these problems are:
- viruses, such as the herpes virus
- bacteria
- mushrooms
- allergy
- hormonal causes
- as a consequence of systemic disease
- genetic predisposition
- mental disorders
- oncological diseases
Differential diagnosis in this case means the exclusion of another disease . It may resemble aphthous inflammation, but it is not. An example is herpetic angina , which is inflammation of the tonsils, ie tonsillitis .
And that includes taking blood for a laboratory test . And this is a blood count or analysis of the level of vitamins and minerals . In some cases, a biopsy of the affected area may be added .
Of course, other additional examinations are chosen by an expert according to the symptoms that occur.
In more difficult cases , examinations such as allergiological , immunological , genetic or microbiological examinations are performed .
Course
An ulcer is formed, which is initially yellowish . Later, its color changes to white to gray . The edge is lined by a sharp border that protrudes slightly above the plane of the intact mucosa. It is reddened around the ulcer .
Due to the healthy mucosa, the ulcer is only slightly below the level. It is painful and worsening of discomfort will cause irritation. As is the case with food, and even worse if it is salty, spicy or sour. There is only one, but a maximum of 6.
Its shape resembles a circle or oval, with a maximum size of 4 mm. These difficulties usually subside within 10 days. Even without special treatment.
This mild course indicates small aphthae .
In the case of large aphthae , the course is more intense . The duration is extended to a month . After healing, a scar often forms at the ulcer site.
This type is characterized by frequent recurrence , ie recurrence .
There is usually only one mucosal defect , but also several , however, a maximum of about 6. It happens that one ulcer heals and then the other appears.
The size of the ulcer can be 1 cm or more.
Herpetiform aphthae occur in the highest number , per piece of mucosal defects . Especially on the tongue. Here, small and numerous ulcers form, which can merge with each other.
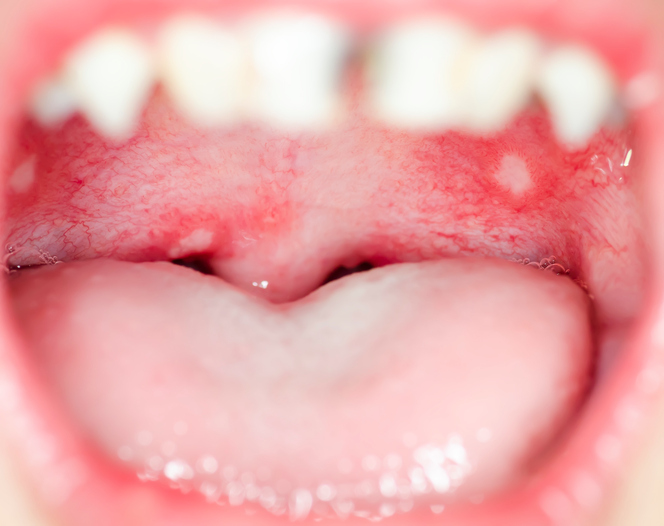
Their pain is of high intensity . Although they resemble herpes infection, hence their name, they do not carry the herpes virus. And so they are not infectious .
It is difficult to estimate how aphthous inflammation will take place. They occur in children or adults. It occurs only once in a lifetime or only once a year, or repeatedly. This factor then also influences the subsequent diagnosis and treatment.
They most often bother people between the ages of 11 and 35.
Women and hormonal changes or pregnancy
We know that the exact cause of the formation of aphthae is not known. However, it is also known that they can also form during hormonal changes, whether during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
During pregnancy, there is a higher demand for minerals and vitamins. It happens because aphthae arise due to a lack of these substances needed by the body. Another cause is a change in immune processes during pregnancy.
Aphthae do not have a negative effect on pregnancy and the fetus.
Prevention is important
Prevention is what we should consider before the outbreak of the disease itself. And not just in this case. A sufficient degree of oral hygiene is important before difficulties occur and during the onset of aphthae .
You will also find interesting information in the articles:
How to choose a suitable toothbrush?
How to have healthy teeth
An increased incidence rate should also be expected in children due to insufficient knowledge and skills in brushing teeth and oral hygiene. That is why it is important to teach them.
Injury and injury in the mouth can be caused by poor handling of the brush, but also by a poorly made denture or dental appliance.
Known causes include, for example:
- traumatic injury in the oral cavity
- toothbrush
- machine
- by injection at the dentist
- bite on the inside of the lip
- tongue bite
- lack of minerals and vitamins
- iron
- vitamin B6
- folic acid, including vitamin B9
- vitamin B12
- food allergies - such as apples, pears, peas or carrots
It is good to remember these causes and set preventive and regime measures.
A proper and healthy lifestyle is also important. A suitable and varied diet will ensure plenty of minerals and vitamins. If the problem is weakened immunity, the cause must be addressed.
Disease Behcet, disease = disease
An illness whose cause is unknown . The prerequisite may be a genetic predisposition , an autoimmune disease or a virus infection . A mutual combination is conceivable. It can also occur familially.
This disease is manifested by a triad of symptoms such as:
- numerous aphthae in the oral cavity
- aphthous ulcers in the genital area
- hypopyoniritis - eye disease
The disease is rare . It mainly affects the population in areas of the world such as Japan, China, Korea, Turkey, Tunisia. It most often starts in the 20th to 35th year of life, especially in men.
The manifestation is the occurrence of aphthae in the oral cavity . Plus, defects and ulcers form on the genitals . In men, it is mainly on the scrotum, ie the scrotum. Less often on the penis. In women, the lips are mainly affected.
Subsequently, the eyes are affected. Both eyes are affected . In most, within three years of the onset of the disease.
Subsequently, it also has a negative effect on other organ systems . And this is, for example, the skin, blood vessels, neurological and digestive system or joints.
You can also find information in the document: Recurrent aphthae and Behcet's disease .
How it is treated: Aphthae
Aphthae: Treatment is local and symptomatic. What medicines will help?
Show moreGallery